-2.jpg?width=240&name=images%20(5)-2.jpg) Most large architecture and engineering firms operate their accounting system on an accrual basis. Most individuals operate their individual “accounting system” on a cash basis (e.g., your checkbook is basically a cash accounting system).
Most large architecture and engineering firms operate their accounting system on an accrual basis. Most individuals operate their individual “accounting system” on a cash basis (e.g., your checkbook is basically a cash accounting system).
The primary difference between the two methods is a matter of timing! The point in time that a financial action occurs and when the results of this action are recorded in the financial reports is different for cash and accrual systems.
A COMPARISON OF CASH AND ACCRUAL BASIS ACCOUNTING
Cash Method
Using the cash method of accounting, you record transactions when they affect cash:
-
Record income (revenue) when your client pays you
-
Record expenses when you write the check
This method can be preferable for tax reporting, but it generally provides less-than-accurate management information because of the lag time between when costs are incurred and payment is received.
Accrual Method
Using the accrual method, the firm records transactions when they are recognized by the accrual rules, rather than when cash changes hands.
-
Revenue is recorded when it is earned and as close as possible to when the costs to create it are incurred
-
Expenses are recorded when they are incurred (e.g., when the bill is received, not when it is paid)
Accrual accounting affects the following financial accounts:
-
Work in process (WIP): completed work for which you incurred costs but haven’t sent an invoice
-
Accounts receivable: invoices you’ve sent for which you haven’t received payment
-
Accounts payable: suppliers’ bills you’ve received for services rendered but haven’t paid
-
Accrued expenses: expenses you’ve incurred for which you haven’t received the supplier’s invoice
-
Deferred income taxes: the difference between taxes you owe on the accrual basis and taxes you’ve paid on the cash basis
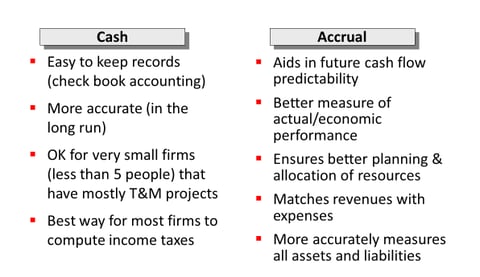
ADVANTAGES OF CASH VS. ACCRUAL
![]() This is just one example of what you can learn in Financial Management For A/E/C Firm Leaders. This hands-on two-day workshop is extremely useful for those who are looking for all levels of financial information – from understanding basic financial indicators your firm should be tracking to interpreting predictive financial metrics for more accurate financial forecasting. Fortunately, a few tweaks in some key financial metrics can dramatically reduce the negative cash flow and time it takes to generate positive cash flow in a growing firm.
This is just one example of what you can learn in Financial Management For A/E/C Firm Leaders. This hands-on two-day workshop is extremely useful for those who are looking for all levels of financial information – from understanding basic financial indicators your firm should be tracking to interpreting predictive financial metrics for more accurate financial forecasting. Fortunately, a few tweaks in some key financial metrics can dramatically reduce the negative cash flow and time it takes to generate positive cash flow in a growing firm.